Why does the U.S. have so many tornadoes?
Tornadoes occur worldwide; they are a part of severe convective storms. Yet, why are there so many tornadoes in the United States? Why does the Midwest have a nickname of “Tornado Alley”?
The answer is a lot less complicated than you might think. There are two ingredients needed to make any type of tornado: contrasting air masses and instability. In fact, some parts of the world are actually more prone to tornadic activity than others, particularly the mid-latitudes between 30 and 50 degrees North and South. The mid-latitudes are areas in which there are generally two air masses that meet each other. For example, a cold air mass from the North may meet a warm air mass from the South. When these two air masses meet, there is more of a chance for severe weather to occur.
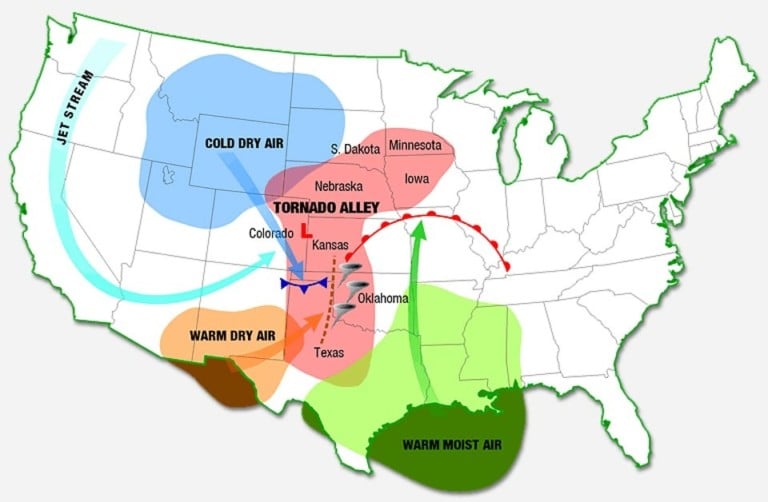
In the United States, there are generally three air masses that meet each other instead of just two. And you guessed it- these three air masses meet in the Midwest.
Cold, dry air from Canada heads south, and Warm, dry air from Mexico heads east to meet in the Midwest. The United States also has a tropical air mass thrown into the mix, and warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico also heads north to meet in this region as well. The addition of this third air mass helps increase the instability in this region, thus increasing the chance for tornadoes to occur.
The contrasting air masses are the first ingredient. Now, there are two more missing pieces to help explain this puzzle. The majority of tornadoes occur in the spring. Tornadoes occur when air mass contrasts are the greatest, so they would not occur in the summer or the winter. However, the spring produces great air mass contrasts because the Northern latitudes in Canada are still relatively cool, but the tropical air from the Gulf of Mexico is beginning to warm up significantly. Why Spring, though, and not Fall?
This is the third piece to the puzzle. In the fall, the days are growing shorter and shorter, and the overall angle and heat of the sun is decreasing. The opposite is true in the spring. In the spring months, the days are growing longer, and the overall temperatures are increasing as the sun goes higher and higher into the sky. The extra-long days help increase the instability, which is why these strong tornadoes occur in the spring rather than the fall.
To put it simply, the United States has the same two major conditions that favor the formation of tornadoes:
- Air mass contrasts
- Instability and a high sun angle
The only difference is, the United States has three contrasting air masses, rather than just two. The difference this makes sure is apparent; the U.S. as a whole sees over 1,000 tornadoes each year!
-Emily Lewis