Below normal hurricane season in the Atlantic and a record breaking season in the Pacific
The Atlantic hurricane season is officially from June 1 to November 30, meaning it is officially over. These dates were set based on 97% of tropical activity, and of course there have been hurricanes that occurred outside of these six months. The Atlantic has a peak season from the months of August through October, with 96% of the major hurricanes, categories 3, 4 and 5 occurring during this time, as well as 87% of minor hurricanes, categories 1 and 2.
Atlantic Hurricane Season
This year the Atlantic season was below normal with 11 named storms and the eastern and central Pacific was above normal with both regions “shattering all-time records.” According to the National Hurricane Center, the Atlantic hurricane season produced 11 named storms, including four hurricanes (Danny, Fred, Joaquin and Kate), with Danny and Joaquin becoming major hurricanes.
Although the four hurricanes did not make landfall in the United States, two tropical storms did cause some damage. Tropical Storms Ana struck the coast of North Carolina and caused wind damage, beach erosion, and one direct death in North Carolina. Bill produced heavy rains and flooding as it moved across the eastern part of Texas and into Oklahoma. Hurricane Joaquin is the first Category 4 hurricane to impact the Bahamas during the month of October since 1866.
The season was expected to be below normal due to El Niño. Lead seasonal hurricane forecaster at NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center, Gerry Bell, Ph.D., says, “El Niño intensified into a strong event during the summer and significantly impacted all three hurricanes seasons during their peak months.”
He also added that El Niño suppressed the Atlantic season by producing strong vertical wind shear combined with increased atmospheric stability, stronger sinking motion and drier air across the tropical Atlantic, all which made it more difficult for storms to form and strengthen.
On the other hand, El Niño also allowed for the weakest vertical wind shear on record for the eastern and central Pacific, fueling the hurricane season.
Pacific Hurricane Season
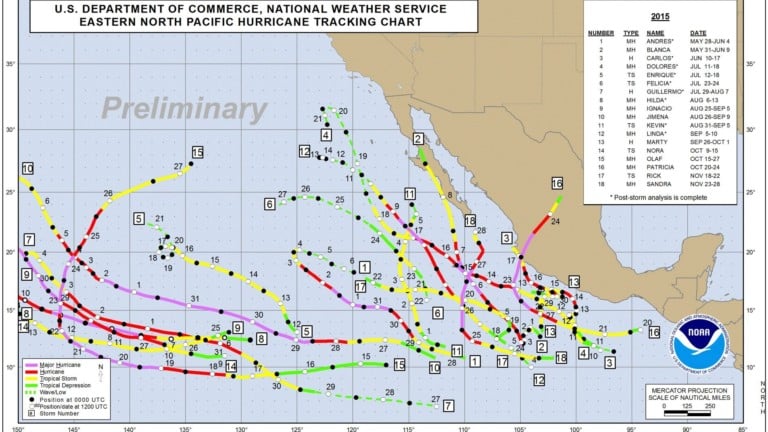
The eastern Pacific season was well above normal with 18 named storms, including 13 hurricanes, with nine of them becoming major hurricanes, categories 3, 4 and 5. Hurricane Patricia was named the strongest hurricane on record in the Western Hemisphere, in terms of wind speed at 200 miles per hour and lowest pressure at 879 millibars. Hurricane Sandra, with sustained winds of 145 miles per hour was named the strongest hurricane in the eastern Pacific so late in the season. This was the first year since reliable data began in 1971 that the eastern Pacific saw nine major hurricanes.
The central Pacific also had a record breaking season with 14 named storms, including eight hurricanes, with five becoming major hurricanes. This is the most active season since 1971. At one point there were three major hurricanes at once (Ignacio, Kilo and Jimena), this was the first time that was ever recorded.